

Once they pay the bill, the $550 in office supplies is now a paid expense.Īnother example of a paid versus incurred expense would be monthly rent.
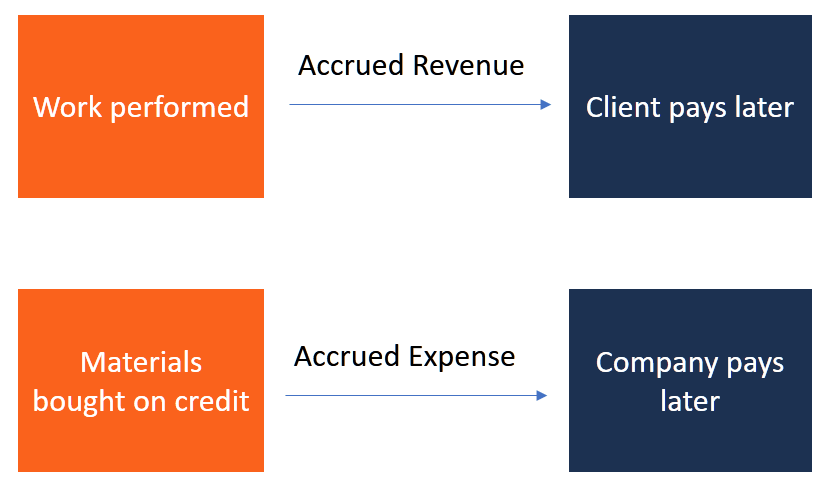
They are billed for the products, and the accounting department lists this as an incurred expense in their records. For example, a company may have $550 in office supplies delivered to the office. In other words, an expense incurred is the cost when an asset is consumed.Ī paid expense has been paid off by the company. Incurred expenses have been charged or billed but are not yet paid. The difference between an incurred expense and a paid expense is whether an outstanding fee has been reimbursed. Related: Costs vs Expenses: Definitions and Examples The difference between incurred and paid expenses Until the loan is paid off, it will be considered part of this category. Loans: Businesses incur expenses when they borrow money. Utilities: The daily costs of phones, the internet, power and air conditioning or heating are all incurred expenses because they are paid on a monthly basis. Companies usually pay these costs once the product is sold. This includes the overhead for any machinery used, power and distribution. Manufacturing: Companies incur costs making a product. Raw materials like metal or wood used in manufacturing) or daily business use (like office supplies) are considered incurred costs. Materials: Up-front like the materials needed by a company either for production (like If companies purchase their own building, a mortgage becomes an incurred expense as well - unless they pay cash. Rent: Between payments, rent is considered an incurred cost to a business. In the time between recurring payments, employee labor is an incurred cost. Most businesses pay employees every two weeks. Payroll: The price of labor is considered an incurred expense since an employee performs a service before they are paid. Setting a monthly date for payment also helps accountants track expenses to create budgets and financial reports. Incurred expenses can include the following:Ĭredit cards: Businesses charge expenses on credit to help control the flow of cash out of a company's account. Related: What Are Accrued Expenses? (Definition and Examples) Examples of incurred expenses They often defer these costs to be paid on credit to help manage their financial resources-however, a company is still responsible for any expenses incurred by operating their business. Any time a business makes a purchase but has not paid for it yet is an incurred expense.Ĭompanies incur expenses to manage the daily needs of their business. Incurred expenses refer to fees that have been charged to a business but have not yet been paid by the company Since these charges will be paid in the future, they're also considered accrued expenses until they are paid off. In this article, we define incurred expenses, give examples of expenses incurred and answer common questions about the term. Certain expenses are necessary and a company makes payments later, just as you would on a personal credit card.
Neither Holdings nor the Parent Borrower will permit Consolidated Lease Expense associated with Capital Expenditures to exceed 30% of Capital Expenditures for such fiscal year.A business has to spend money in order to make a profit. Phil Ercolini stated that the analysis of the MLDA is a departure from his previous experience, and that he is pro-development.įuture minimum lease payments and operating lease expense are as follows:Operating CapitalLeases Leases($ in millions) 2009$ 142$ 66201012928201194262012791720137032014 and subsequent years 359 5 Total$ 873 $ 145Less imputed interest on capital leases at an average rate of 5.3% (6) Present value of minimum lease payments included in debt $ 139 Operating Lease Expense 2008 Contingent rents are primarily comprised of usage-based rent paid to other railroads for joint facility operations.įor purposes of this Lease, the term "Aggregate Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio" shall mean with respect to the twelve month period of time ending on the date of calculation, the ratio calculated for such period of time of (a) the sum of Net Income, Depreciation and Amortization, Interest Expense and Operating Lease Expense, less a corporate overhead allocation in an amount equal to 4% of Aggregate Gross Sales, to (b) the sum of the Operating Lease Expense and the Equipment Payment Amount.
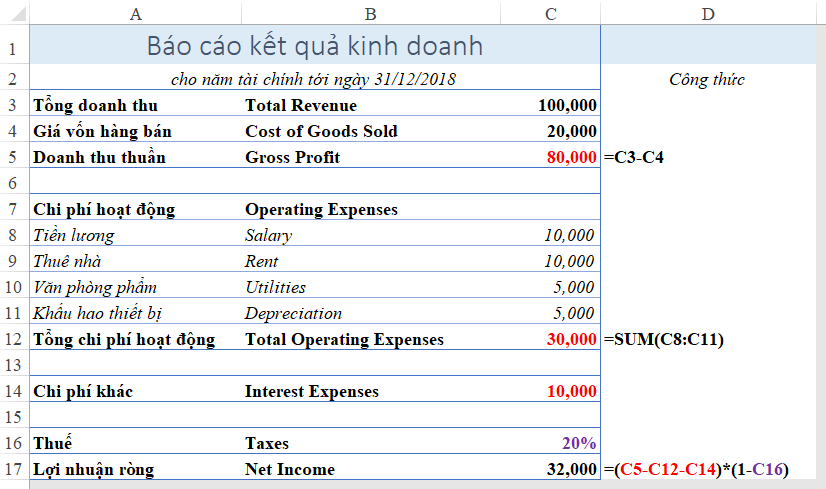
Cach tinh incurred expenses pro#
Cach tinh incurred expenses plus#
For example, Lease Expense for 2021 is base rent ($192,000) plus Taxes and CAM ($36,000) for a total of $228,000, which matches the proforma.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
